As you plan for retirement, one of the most important financial decisions you’ll make is how to save for your golden years. Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) offer a powerful and tax-advantaged way to build a substantial retirement nest egg.

What is an IRA?
An IRA is a personal retirement savings account that allows you to invest and grow your wealth for your future. Unlike employer-sponsored retirement plans like 401(k)s, IRAs provide greater flexibility and control over your investments.
Key Advantages of IRAs
- Tax Benefits: IRAs offer significant tax advantages, including tax-deferred growth or tax-free withdrawals.
- Investment Flexibility: IRAs provide a wider range of investment options compared to some employer-sponsored plans, allowing you to diversify your portfolio and tailor your strategy to your risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Accessibility: IRAs are available to individuals regardless of their employment status, making them a versatile retirement savings tool.
- Contribution Limits: IRAs have annual contribution limits, which can vary depending on your age and income.
- Early Withdrawal Penalties: Be aware of the potential penalties for withdrawing funds before reaching the required age.
Types of IRAs
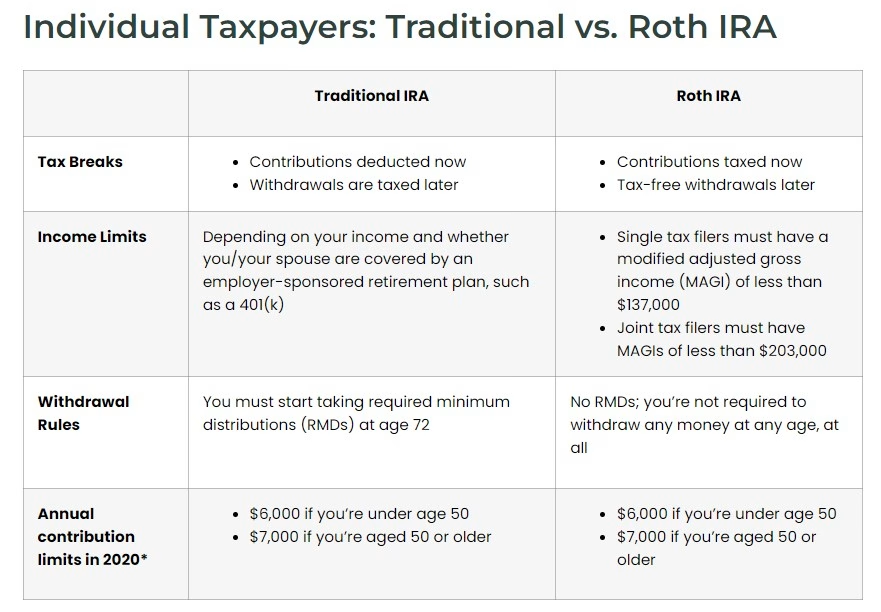
- Traditional IRAs:
- Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income.
- Withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income.
- Suitable for those in higher tax brackets now but anticipate being in a lower bracket during retirement.
- Roth IRAs:
- Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, but withdrawals are tax-free.
- Ideal for those who anticipate being in a higher tax bracket during retirement.
- Income eligibility limits apply.
- SEP IRAs:
- Designed for self-employed individuals and small business owners.
- Offers higher contribution limits compared to traditional IRAs.
- SIMPLE IRAs:
- Employer-sponsored plans for small businesses.
- Allows for matching contributions from employers.
- Rollover IRAs:
- Used to transfer funds from other retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s, to an IRA.
- Provides flexibility and potentially lower fees.
How IRAs Work
- Investment Options: IRAs allow you to invest in a variety of financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, ETFs, and mutual funds.
- Early Withdrawal Penalties: Withdrawing funds before reaching the required age (usually 59 1/2) may result in a 10% penalty and income taxes.
- Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs): You must start taking RMDs from traditional IRAs after reaching a certain age.
Why You Need an IRA
- Supplement Your Retirement Savings: IRAs can help you save more for retirement, especially if your employer-sponsored plan has contribution limits.
- Expand Your Investment Options: IRAs offer a wider range of investment choices compared to some employer-sponsored plans.
- Manage Your Taxes: IRAs can provide tax benefits, either through tax-deferred growth or tax-free withdrawals.
- Gain Control and Flexibility: IRAs give you more control over your retirement savings and allow you to easily transfer funds between accounts.
Choosing the Right IRA
The best IRA for you depends on your individual circumstances, including your income, age, retirement goals, and risk tolerance. Consider consulting with a financial advisor to help you make an informed decision.
Conclusion
IRAs are powerful tools that can significantly enhance your retirement savings journey. By understanding the different types of IRAs, their benefits, and how they work, you can make informed decisions and take steps toward a financially secure future.
